Have you ever wondered what those numbers on your pulse oximeter really mean? We’re talking about more than just oxygen saturation.
There’s something called the perfusion index (PI) that often gets overlooked.
PI measures how strong your pulse is at the spot where you’ve clipped the oximeter, like your fingertip or earlobe. This is super important because a weak pulse can throw off the whole reading. So, what’s a normal PI, and why should you care?
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about PI, from what it measures to normal ranges.
We’ll even show you how to use your oximeter correctly to get the most accurate results. Understanding PI is key to monitoring your blood oxygen and overall health.
What is Normal PI on Oximeter?
- PI measures your pulse strength at the sensor site.
- Normal PI ranges from 0.02% (very weak) to 20% (very strong).
- Your “normal” PI can vary depending on individual factors.
- Consistently low or changing PI may indicate a health issue.
- Accurate readings depend on proper oximeter use.
What is the Perfusion Index (PI)?
So, what’s this “perfusion index” (PI)? It’s simply a way to measure how strong your pulse is where your pulse oximeter is clipped on, like your fingertip or earlobe. It’s similar to checking your pulse manually, but with light.
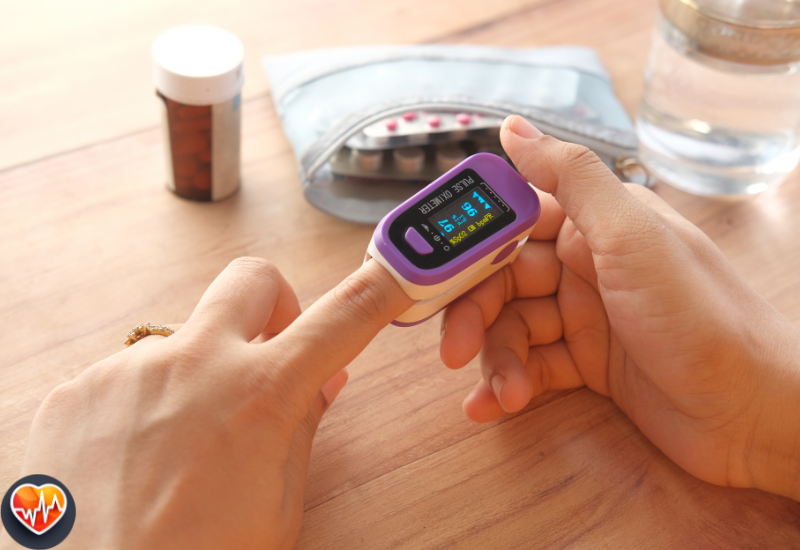

Pulse oximeters use light to measure both the oxygen in your blood and your pulse strength.
They shine two colors of light through your finger, and the amount of light absorbed changes with each heartbeat. The oximeter analyzes these changes to give you your pulse rate and PI.
A good, strong pulse is crucial for accurate oxygen readings. If your pulse is weak, the oximeter might struggle, leading to unreliable results. That’s why PI is important.
A normal PI can vary, but generally, a higher PI means better blood flow to your fingers and toes.
A lower PI could indicate poor perfusion or other health issues like blood clots or peripheral artery disease. We’ll dive into that more in the next section.
Understanding Normal PI Ranges
Now that we know what PI is let’s talk about what’s considered “normal.” Generally, a normal perfusion index (PI) reading on your pulse oximeter falls between 0.02% and 20%. A higher PI, closer to 20%, means your pulse is strong and there’s good pulsatile blood flow to the area where you’re measuring, like your middle fingertip or earlobe. This indicates good peripheral perfusion.
Here’s the catch: what’s normal for you might be different from someone else. Your PI can change depending on things like:
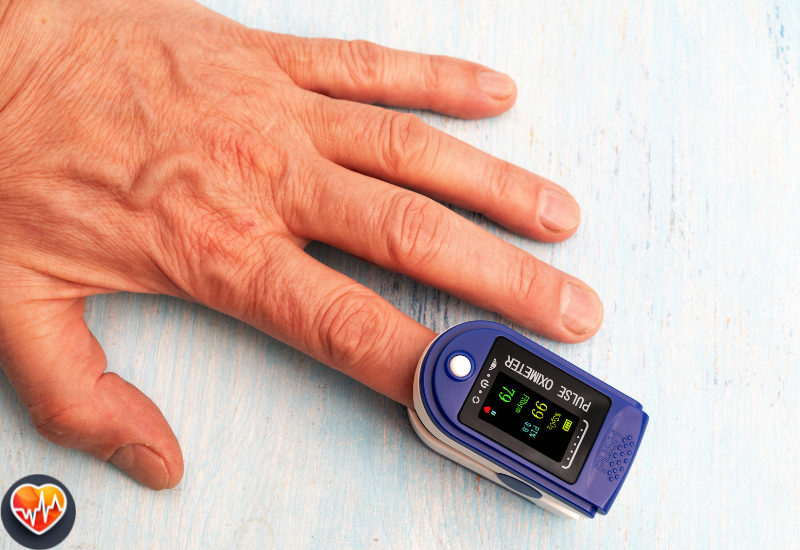
- Where you’re measuring: Fingertips tend to have higher PI readings than earlobes.
- Your age: Older folks might naturally have lower PI values.
- Your overall health: Conditions like peripheral artery diseases can lower PI.
- Temperature: Cold fingers can lead to lower PI readings.
Don’t sweat it if your oximeter reading isn’t exactly within the “normal range.” It’s more important to track your own personal trends over time.
If you notice sudden drops or consistently low PI readings, it could be a sign of poor peripheral perfusion, weak pulse strength, or other health issues like non-pulsatile blood flow due to a blood clot.
Keep in mind that PI readings are a tool, not a diagnosis. If you’re concerned about your PI, talk to your doctor. They could help you figure out what’s normal for you and whether any further tests are needed.
How to Use an Oximeter to Measure PI
Using a pulse oximeter to measure PI isn’t rocket science, but a few tricks can help you get the most accurate reading:
- Pick the Perfect Spot: Your middle fingertip is usually the optimal monitoring site, as it typically has good arterial blood flow. However, if your hands are cold, try warming them up first or use your earlobe instead.
- Clip It On Right: Make sure your finger (or earlobe) is snug inside the oximeter but not so tight that it cuts off circulation. It should be comfy, not painful. Avoid putting the sensor on the same side as a blood pressure cuff, which can affect blood flow.
- Stay Still and Chill: Relax! Movement can mess with the reading. Hold your hand still and wait a few seconds for the numbers to settle.
Here are a few more tips:

- Check Your Nails: Remove any dark nail polish, as it can block the light and affect the reading.
- Keep It Clean: Wipe the sensor site with a damp cloth to keep it working properly.
- Don’t Rely on One Reading: Take a few readings over a couple of minutes to get a good average. If your pulse is very weak, it might take longer for the oximeter to get an accurate reading.
That’s it! It’s pretty simple. But if you’re still getting weird readings (like a very weak pulse or a PI of zero), it could mean the sensor isn’t getting a good pulsatile signal from your peripheral tissue.
Try moving the oximeter to a different finger or your earlobe. This can sometimes happen in cases of anesthetic failure or acute illness.
Remember, if your readings are consistently low or you’re worried about your health, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor.
With these tips, you can use your pulse oximeter like a pro! And don’t worry, we’ll cover how to understand those PI readings in the next section.
Interpreting Your PI Reading
Alright, so you’ve got your pulse oximeter reading – what do those PI numbers actually mean? Here’s a simple breakdown of what is normal PI on oximeter:
- High PI (closer to 20%): This is a good sign! It means your pulse is strong and there’s plenty of blood flow to your fingers or earlobe. This indicates good peripheral perfusion. It might even indicate an extremely strong pulse!
- Normal PI (between 0.02% and 20%): Most people fall within this range. The exact “normal” for you depends on where you’re measuring (finger vs. earlobe) and your own unique body and can be affected by several factors. If you’re healthy, this range means your blood flow is doing just fine.
- Low PI (closer to 0.02%): This could mean a few things. Your fingers might be cold, or your circulation might not be great. It could also be a sign of a weak pulse or other health issues.

It’s super important to note that PI is just one part of the picture. Your pulse oximeter reading also shows your oxygen saturation (SpO2), which tolds you how much oxygen is in your blood. Both PI and SpO2 are important for monitoring your health through pulse oximetry.
Why should you care about your PI?
- Early Warning: Changes in your PI can sometimes be an early warning sign of health problems, even before you notice any symptoms.
- Track Your Health: By keeping tabs on your PI over time, you can see how it changes and get a better idea of what’s normal for you.
- Monitor Conditions: If you have a health condition like heart disease or diabetes, tracking your PI can help you monitor your circulation and overall health and track disease progression.

Important Note: PI readings vary depending on where you’re measuring. For example, your PI on your left middle finger might be different from your PI on your ear lobe. This is due to differences in the amount of arterial blood and other factors at each measurement site. This is why it’s important to choose a consistent monitoring site so you can accurately track changes in your readings.
Remember: Don’t panic if your PI seems a bit low. It’s always best to talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your readings or your user’s pulse strength. They can help you understand what’s normal for you and recommend any further testing if needed.
Practical Tips for Accurate PI Readings
Getting the hang of using your pulse oximeter and understanding PI is great, but let’s dive into some simple tips to make sure your readings are as accurate as possible:
- Warm It Up: Cold fingers can mean poor blood flow, so warm up your hands before taking a reading. You can rub them together or run them under warm water. This helps ensure accurate measurement of oxygen saturation and PI.
- Chill Out: Movement can mess with the oximeter’s ability to detect your pulse. Relax your hand and try not to move it while the oximeter does its thing.
- Ditch the Nail Polish: Dark nail polish can block the light the oximeter uses. If you’re wearing it, take it off before measuring.
- Keep It Clean: Wipe the oximeter’s sensor with a damp cloth regularly. This helps keep it working properly and prevents any gunk from getting in the way.
- Check the Battery: Make sure your pulse oximeter has a fresh battery. A low battery can sometimes affect the accuracy of readings.
Here are a few more things to keep in mind:

- Different Fingers, Different Readings: Don’t be surprised if the PI on your right middle finger is a little different from the PI on your left. Blood flow can vary a bit between fingers and other monitoring sites. Just try to be consistent with which finger you use so you can accurately track changes in your readings.
- Non-Pulsing Blood: Most pulse oximeters need pulsating blood to measure PI. If you have very poor circulation, the oximeter might not be able to get a reading at all.
- Not All Oximeters Are Created Equal: Some pulse oximeters are better at measuring PI than others. If you’re concerned about accuracy, talk to your doctor or pharmacist about which model might be best for you. Some models might be more sensitive at detecting a wider range of PI’s values.
Remember, the goal is to get an accurate measure of your PI so you can track your health over time. With a little practice and these simple tips, you’ll be a pulse oximeter pro in no time!
PI and Your Health
You might be wondering, “Why should I care about PI?” Well, it turns out that PI can give you some helpful clues about your overall health, especially when it comes to your blood circulation.
Here’s the deal: PI gives you a peek into how well your blood is flowing to your fingers and toes, also known as peripheral circulation. This is important because good blood flow is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to your tissues and for accurate measurement of oxygen saturation.
Think of it like a highway system. Your blood vessels are the roads, and your blood cells are the cars carrying important cargo. PI tells you how smoothly the traffic is flowing in your patient’s peripheral tissue. If there’s a traffic jam (low PI), it could mean trouble.
Here’s why paying attention to PI matters:

- Early Warning System: Changes in PI can sometimes be an early indicator of problems with your blood vessels, even before you notice any symptoms. For example, a sudden drop in PI could signal a blockage in your blood flow, which could be due to a blood clot or other issues.
- Tracking Health Conditions: If you have a condition that affects your circulation, like diabetes or peripheral artery diseases, monitoring your PI can help you keep tabs on how well your treatment is working. Changes in PI can help track disease progression and alert you to potential complications.
- Better Oxygen Readings: PI can also help your doctor get more accurate readings of your oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rate. This is because a good pulsatile signal is necessary for reliable measurements.
Now, let’s be clear: PI isn’t a magic crystal ball. It won’t tell you everything about your health, and it can’t diagnose specific conditions. But it’s a useful tool that, when understood within the normal perfusion index (PI) ranges, can give you and your doctor valuable information about your circulation. It can also help identify instances of non-pulsatile signals, which may indicate the need for further evaluation.
By understanding your PI readings and working with your doctor, you could make informed decisions about your health and get the proper management you need to stay healthy and active.
Conclusion
Well, there you have it! You’ve learned all about PI, the secret weapon hidden within your pulse oximeter. Now you know that it’s not just about measuring oxygen saturation, but also about checking your pulse strength.
Remember, PI can vary, and what’s normal for you might not be the same for someone else. Keep an eye on your own trends, and if something seems off, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor.
By understanding PI’s values range & how it fits into the bigger picture of your health, you’re taking a big step towards taking control of your well-being.
So next time you clip on that pulse oximeter, you’ll know exactly what those numbers mean and how they can help you stay on top of your health.
While PI typically occurs alongside oxygen saturation readings on most pulse oximeters, its value goes beyond just showing how well the device is working.
It offers insights into your circulation, potential health issues, and even helps with early detection of certain conditions. It might not always be the main focus, but understanding PI can be a game-changer when it comes to managing your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What if my PI is too low?
A low PI might simply mean your hands are cold, or it could indicate poor circulation. If you’re concerned, warm up your hands and recheck. If it’s still low or you have other symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Can a low PI be dangerous?
While a low PI itself isn’t necessarily dangerous, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health issue like poor circulation or a weak pulse. It’s best to consult your doctor if you’re worried.
Does the type of pulse oximeter matter for measuring PI?
Yes, different pulse oximeters have varying degrees of accuracy when measuring PI. If you need precise readings, consider investing in a higher-quality device.
Can I improve my PI reading?
Yes! Simple things like warming your hands, staying hydrated, & exercising regularly can improve blood flow and potentially boost your PI.
Why does my PI fluctuate throughout the day?
Your PI can change due to factors like activity level, stress, temperature, and even medication. It’s normal for PI to fluctuate slightly, but sudden or significant changes might warrant a chat with your doctor.